Difference between revisions of "Bovis scale"
m |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[image:Bovis.jpg|thumb|right|Bovis-units according to A. Bovis|300px]] | [[image:Bovis.jpg|thumb|right|Bovis-units according to A. Bovis|300px]] | ||
| − | The '''Bovis | + | The '''Bovis scale''' (''Bovis units'') is used by [[Radiesthesia|radiesthesists]] (dowsers) and adherents of [[geomancy]] to describe the "strength" of an alleged "subtle energy" or "life energy", or an alleged "cosmo-telluric energy". This unit is not accepted scientifically and is of [[pseudoscience|pseudoscientific]] character. |
==The origins, and the inventor A. Bovis== | ==The origins, and the inventor A. Bovis== | ||
[[image:A_Bovis.jpg|A. Bovis (putative Antoine Bovis)|left|200px|thumb]][[image:Andre_Bovis.jpg|André Bovis|left|150px|thumb]] | [[image:A_Bovis.jpg|A. Bovis (putative Antoine Bovis)|left|200px|thumb]][[image:Andre_Bovis.jpg|André Bovis|left|150px|thumb]] | ||
| − | The origins of the term "Bovis" is unclear. According to different sources the Bovis | + | The origins of the term "Bovis" is unclear. According to different sources, the Bovis scale was named after an alleged French physicist, radiesthesist, inventor, and bioler smith by the name of Bovis. His first name is referred as Anton<ref>http://www.energynics.com/bovis-scale.shtml</ref>, Antoine<ref>http://www.jenskleemann.de/wissen.php4?p=b/bo/bovis.html</ref><ref>http://www.skeptic.com/junior_skeptic/issue23/translation_Bovis.html</ref>, "André Bovis from Nice"<ref>http://www.conscienceverte.fr/la-regle-de-bovis-%28premiere-partie%29-2-168.html</ref>, or Alfred<ref>http://www.magic-places.ch/Boviseinh.html</ref>. But there are no doubts about his birth date, January 12, 1871 in Nice (France). A. Bovis died November 13, 1947. |
| − | + | Czech radio-technician and pseudo-scientist Karel Drbal, in his book ''The Struggle for the Pyramid Patent'',<ref>Drbal, Karel: The Struggle for the Pyramid Patent. Warner Destiny, 1976)</ref>, asserts that the inventor of the Bovis scale was Antoine Bovis who allegedly owned a hard-ware store, did private radiesthetic studies and worked on a [[Esotericism|esoteric]] pyramid energy. The website "sceptic.com" also mentions one Antoine Bovis.<ref>http://www.skeptic.com/junior_skeptic/issue23/translation_Bovis.html</ref> Sceptic.com shows a book by one "A. Bovis" in which he describes his ''"méthode niçoise de radiesthesie"'' (Nicoise method of radiesthesia) with his ''biometre''. However, the first name Antoine is never mentioned, the author is always described as "Mr. A. Bovis", with a postal address of "Bovis, 15 rue Pertinax, Nice". Apparently, and for unknown reasons, the author decided not to reveal his first name. | |
| − | On the other hand | + | On the other hand there is no doubt that "Mr. A. Bovis" in fact was André Bovis, a boiler smith, inventor, and radiesthesist from Nice in southern France. His grandson Jacques Bovis, who defines himself as a "geobiologist", refers his alleged radiesthetic abilities to his grandfather André Bovis.<ref>http://www.geobiologie.fr/pages_fr/enseignants.php</ref>. |
| − | + | French citizen André Simoneton seems to have made further developments of Bovis's invention, and he spoke of a so-called ''radio vitality'' (radiovitalité). Both Bovis and Simoneton related the Bovis scale to the wellknown length scale Ångström (1 Å = 0,1 nm or 10<sup>−10</sup>m). On an original Bovis scale made by Bovis, the unit Ångström can be seen (see picture). | |
==Bovis reading== | ==Bovis reading== | ||
| − | [[image:Bovismeter1.png|thumb|300px|biometer or bovismeter ( | + | [[image:Bovismeter1.png|thumb|300px|biometer or bovismeter (French: ''biometre'')]] |
| − | During a Bovis | + | During a Bovis "measurement", the dowser walks around the place or approaches a particular object with a device (a pendulum, biotensor or "biometer"). The "measurement" is completed when the dowser declares the local Bovis figure (''"this place has 18000 Bovis"''). Sometimes a second person counts down from a high figure until the dowser asks him to stop counting and to tell the actual figure. |
| − | A | + | A figure of 6,500 is considered "neutral", lower figures affect human "energies" negatively, while higher ones are said to have a positive effect.<br> |
==The values== | ==The values== | ||
| − | A Bovis | + | A Bovis figure of 6,500 is considered "neutral", lower figures affect human "energies" negatively, higher figures are said to have a positive effect. |
| − | + | Figures above 10,000 are in the "ethereal range" and considered to be [[Place of Power|places of power]] | |
| − | Bovis | + | Bovis figures according to German dowser Markus Schirner<ref>Schirner M, Pendel-Set, Schirner-Verlag, ISBN:3-930944-65-0</ref> |
{| | {| | ||
|0 - 2000 || crossings of two or more disturbing zones; immune dysfunction; arrest of growth | |0 - 2000 || crossings of two or more disturbing zones; immune dysfunction; arrest of growth | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
|7000 - 8000 || best value / full vitality | |7000 - 8000 || best value / full vitality | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |9000 - 10000 || too high in case of long | + | |9000 - 10000 || too high in case of long exposure |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |10000 - 13500 || energetic | + | |10000 - 13500 || energetic and etheric zones of the human body |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |13500 - 18000 || spiritual, sacred and esoteric places | + | |13500 - 18000 || spiritual, sacred, and esoteric places |
|- | |- | ||
|18000 and higher || regions of cosmic rays | |18000 and higher || regions of cosmic rays | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Visible light has | + | Visible light has a wavelength between 3,800 Å and 7,800 Å. These wavelengths correspond to frequencies between 789 and 385 THz. Therefore, the declaration of "full vitality" will correspond to red light and have an energy of 2 eV per photon, ultra-violet light having an energy of 3 eV per photon (1 eV = 1,6 · 10<sup>-19</sup> Joule). |
| − | == | + | ==Criticism== |
| − | [[image:Vibracell.jpg|advertisement for a comestible using Bovis | + | [[image:Vibracell.jpg|Example of advertisement for a comestible using "Bovis values"|420px|thumb]] |
| − | The Bovis | + | The Bovis scale is used on a basis of undefined, imprecise or obscure terms like "life energy", "astralic" or "vitality". Furthermore, while established scientific terms (energy, radiation, measurement) are being used, their meaning is not disclosed, an indication of pseudoscience. There is no definition given for the "Bovis units" and there are no known detecting or calibrating instruments for the claimed "subtle energies". Effects deduced from pendulum movements are known to be influenced by the Carpenter effect. |
| − | == | + | Some sources, among them inventors Bovis and Simoneton, relate their Bovis values to the known unit Ångström while speaking about "wavelength" of alleged measured radiations. Some authors also speak about "Bio-Ångström", making it further difficult to understand what they are talking about. Using Bovis values as length units, they can be used to assign an energy in its physical meaning. But by doing this, an increasing Bovis value will rather assign decreasing energies (as known in physics), because the wavelenghth of an electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to its frequency, and not increasing energy, as supporters of the Bovis concept state. Also, using Bovis figures as Ångström, the claimed radiation energy would be visible. |
| + | |||
| + | Sometimes Bovis figures are used to diagnose diseases in humans. There is no rational basis for this pseudo-medical use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OtherLang|ge=Bovis-Einheit|en=Bovis scale}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Literature== | ||
* Simoneton, André: Radiations des aliments, ondes humaines et sante, Paris 1949 | * Simoneton, André: Radiations des aliments, ondes humaines et sante, Paris 1949 | ||
* Simoneton, André: Radiovitalite des des aliements - hypotheses sur la vie et la sante (1949) | * Simoneton, André: Radiovitalite des des aliements - hypotheses sur la vie et la sante (1949) | ||
| Line 54: | Line 60: | ||
==Weblinks== | ==Weblinks== | ||
*[http://skeptic.com/downloads/Antoine_Bovis_Booklet.pdf "Sceptic.com": expose of A. Bovis (french)] | *[http://skeptic.com/downloads/Antoine_Bovis_Booklet.pdf "Sceptic.com": expose of A. Bovis (french)] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==references== | ==references== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:52, 1 March 2013
The Bovis scale (Bovis units) is used by radiesthesists (dowsers) and adherents of geomancy to describe the "strength" of an alleged "subtle energy" or "life energy", or an alleged "cosmo-telluric energy". This unit is not accepted scientifically and is of pseudoscientific character.
The origins, and the inventor A. Bovis
The origins of the term "Bovis" is unclear. According to different sources, the Bovis scale was named after an alleged French physicist, radiesthesist, inventor, and bioler smith by the name of Bovis. His first name is referred as Anton[1], Antoine[2][3], "André Bovis from Nice"[4], or Alfred[5]. But there are no doubts about his birth date, January 12, 1871 in Nice (France). A. Bovis died November 13, 1947.
Czech radio-technician and pseudo-scientist Karel Drbal, in his book The Struggle for the Pyramid Patent,[6], asserts that the inventor of the Bovis scale was Antoine Bovis who allegedly owned a hard-ware store, did private radiesthetic studies and worked on a esoteric pyramid energy. The website "sceptic.com" also mentions one Antoine Bovis.[7] Sceptic.com shows a book by one "A. Bovis" in which he describes his "méthode niçoise de radiesthesie" (Nicoise method of radiesthesia) with his biometre. However, the first name Antoine is never mentioned, the author is always described as "Mr. A. Bovis", with a postal address of "Bovis, 15 rue Pertinax, Nice". Apparently, and for unknown reasons, the author decided not to reveal his first name.
On the other hand there is no doubt that "Mr. A. Bovis" in fact was André Bovis, a boiler smith, inventor, and radiesthesist from Nice in southern France. His grandson Jacques Bovis, who defines himself as a "geobiologist", refers his alleged radiesthetic abilities to his grandfather André Bovis.[8].
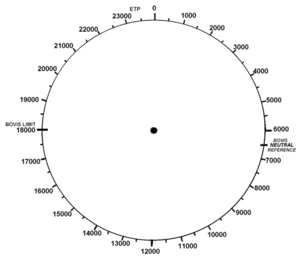
French citizen André Simoneton seems to have made further developments of Bovis's invention, and he spoke of a so-called radio vitality (radiovitalité). Both Bovis and Simoneton related the Bovis scale to the wellknown length scale Ångström (1 Å = 0,1 nm or 10−10m). On an original Bovis scale made by Bovis, the unit Ångström can be seen (see picture).
Bovis reading
During a Bovis "measurement", the dowser walks around the place or approaches a particular object with a device (a pendulum, biotensor or "biometer"). The "measurement" is completed when the dowser declares the local Bovis figure ("this place has 18000 Bovis"). Sometimes a second person counts down from a high figure until the dowser asks him to stop counting and to tell the actual figure.
A figure of 6,500 is considered "neutral", lower figures affect human "energies" negatively, while higher ones are said to have a positive effect.
The values
A Bovis figure of 6,500 is considered "neutral", lower figures affect human "energies" negatively, higher figures are said to have a positive effect.
Figures above 10,000 are in the "ethereal range" and considered to be places of power
Bovis figures according to German dowser Markus Schirner[9]
| 0 - 2000 | crossings of two or more disturbing zones; immune dysfunction; arrest of growth |
| 2000 - 6000 | interference zone; detrimental to humans |
| 6500 | neutral |
| 7000 - 8000 | best value / full vitality |
| 9000 - 10000 | too high in case of long exposure |
| 10000 - 13500 | energetic and etheric zones of the human body |
| 13500 - 18000 | spiritual, sacred, and esoteric places |
| 18000 and higher | regions of cosmic rays |
Visible light has a wavelength between 3,800 Å and 7,800 Å. These wavelengths correspond to frequencies between 789 and 385 THz. Therefore, the declaration of "full vitality" will correspond to red light and have an energy of 2 eV per photon, ultra-violet light having an energy of 3 eV per photon (1 eV = 1,6 · 10-19 Joule).
Criticism
The Bovis scale is used on a basis of undefined, imprecise or obscure terms like "life energy", "astralic" or "vitality". Furthermore, while established scientific terms (energy, radiation, measurement) are being used, their meaning is not disclosed, an indication of pseudoscience. There is no definition given for the "Bovis units" and there are no known detecting or calibrating instruments for the claimed "subtle energies". Effects deduced from pendulum movements are known to be influenced by the Carpenter effect.
Some sources, among them inventors Bovis and Simoneton, relate their Bovis values to the known unit Ångström while speaking about "wavelength" of alleged measured radiations. Some authors also speak about "Bio-Ångström", making it further difficult to understand what they are talking about. Using Bovis values as length units, they can be used to assign an energy in its physical meaning. But by doing this, an increasing Bovis value will rather assign decreasing energies (as known in physics), because the wavelenghth of an electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to its frequency, and not increasing energy, as supporters of the Bovis concept state. Also, using Bovis figures as Ångström, the claimed radiation energy would be visible.
Sometimes Bovis figures are used to diagnose diseases in humans. There is no rational basis for this pseudo-medical use.
Versions of this article in other languages
- Deutsch: Bovis-Einheit
Literature
- Simoneton, André: Radiations des aliments, ondes humaines et sante, Paris 1949
- Simoneton, André: Radiovitalite des des aliements - hypotheses sur la vie et la sante (1949)
Weblinks
references
- ↑ http://www.energynics.com/bovis-scale.shtml
- ↑ http://www.jenskleemann.de/wissen.php4?p=b/bo/bovis.html
- ↑ http://www.skeptic.com/junior_skeptic/issue23/translation_Bovis.html
- ↑ http://www.conscienceverte.fr/la-regle-de-bovis-%28premiere-partie%29-2-168.html
- ↑ http://www.magic-places.ch/Boviseinh.html
- ↑ Drbal, Karel: The Struggle for the Pyramid Patent. Warner Destiny, 1976)
- ↑ http://www.skeptic.com/junior_skeptic/issue23/translation_Bovis.html
- ↑ http://www.geobiologie.fr/pages_fr/enseignants.php
- ↑ Schirner M, Pendel-Set, Schirner-Verlag, ISBN:3-930944-65-0